15/8/2023
The project aimed to view a common technique for digital computers to control the power received via digital means. With the correct equipment, it should be easy to identify.
What is PWM
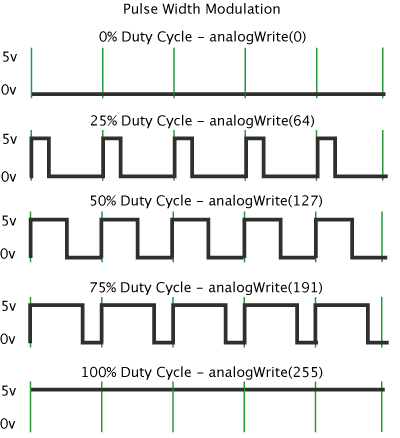
PWM is short for Pulse Width Modulation. By very quickly pulsing it can create an on average lower power and therefore devices like LEDs and other devices will appear as though it is being provided with lower power. On an Oscilloscope it should appear as two separate lines on the oscilloscope in varying lengths as the pulse changes. On an Arduino, this value is between or equal to 0 and 255. It is controlled using the AnalogWrite command. The time between pulses is determined using this value. Where 255 is 0 time between pulses and 0 is infinite.
Equipment
The equipment I used for this project was a 1994 oscilloscope from GoldStar rated for up to 20Mhz and my Arduino the create a basic circuit which would take an analogue input from a potentiometer and convert it into a PWM signal. This allowed me to change the width of the PWM in real-time.
Code
int value;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9200);
}
void loop() {
value = analogRead(A0);
Serial.println(value);
delay(20);
AnalogWrite(value/250)
}
What was Seen
I have provided a video below showing the changes in pulse width on the oscilloscope. Once the pulse width becomes zero the oscilloscope shows a flat line at 0V. When the pulse width is more than one you can see a line above 0 which is the power sent and another line at zero. This represents the different values and when added together over one wavelength an average voltage is provided which can be varied.